Arrange the following bonds in order of increasing bond length: A Comprehensive Guide delves into the fascinating realm of chemical bonding, exploring the intricate relationship between bond order and bond length. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the factors that influence bond length, from the nature of the atoms involved to the effects of resonance and hybridization.
Through engaging explanations and illustrative examples, we will unravel the complexities of bond length and its profound implications in chemistry.
As we embark on this journey, we will delve into the fundamental concepts of single, double, and triple bonds, examining their characteristics and the factors that govern their bond lengths. We will then explore the intriguing relationship between bond order and bond length, demonstrating how the number of shared electron pairs directly influences the distance between atoms.
Furthermore, we will investigate the impact of resonance and hybridization on bond length, showcasing how these phenomena can alter the electronic structure and geometry of molecules.
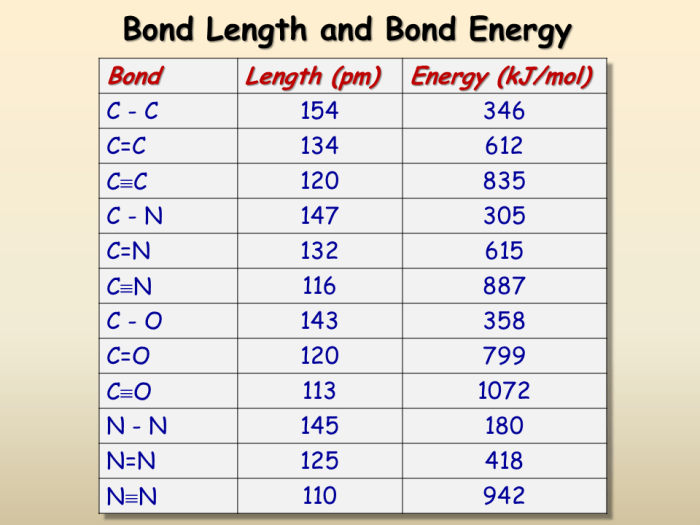
Bond Lengths of Single, Double, and Triple Bonds
Bond length is a crucial parameter in chemistry, providing insights into the nature of chemical bonds. This article explores the bond lengths of single, double, and triple bonds, discussing their characteristics, factors affecting their lengths, and the relationship between bond order and bond length.
Single Bonds
Single bonds are formed by the overlap of one pair of electrons between two atoms. They are the most common type of bond and are typically the longest among single, double, and triple bonds. The bond length of a single bond depends on several factors, including the atomic radii of the bonded atoms and the electronegativity difference between them.
Double Bonds
Double bonds consist of two pairs of electrons shared between two atoms. They are shorter than single bonds due to the increased electron density between the bonded atoms. The bond length of a double bond is influenced by factors such as the hybridization of the bonded atoms and the presence of resonance.
Triple Bonds
Triple bonds are formed by the overlap of three pairs of electrons between two atoms. They are the shortest among single, double, and triple bonds because of the maximum electron density between the bonded atoms. The bond length of a triple bond is primarily determined by the atomic radii of the bonded atoms and the hybridization of the bonded atoms.
Bond Order and Bond Length
Bond order is a measure of the number of electron pairs shared between two atoms. As the bond order increases, the bond length decreases. This trend is observed because the increased electron density leads to stronger electrostatic attraction between the bonded atoms, resulting in a shorter bond length.
Resonance and Bond Length, Arrange the following bonds in order of increasing bond length
Resonance is a phenomenon where a molecule can exist in multiple equivalent Lewis structures. Resonance can affect bond lengths by delocalizing electrons, which reduces the electron density between specific atoms. This delocalization can lead to an increase in bond length.
Hybridization and Bond Length
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals with different shapes and energies. The type of hybridization affects the bond length because it determines the overlap of the atomic orbitals involved in bonding. For example, sp 3hybridization leads to tetrahedral geometry and longer bond lengths compared to sp 2hybridization, which results in trigonal planar geometry and shorter bond lengths.
FAQ Compilation: Arrange The Following Bonds In Order Of Increasing Bond Length
What is bond length?
Bond length refers to the distance between the nuclei of two atoms that are chemically bonded to each other.
How does bond order affect bond length?
Bond order is directly proportional to bond length, meaning that as the bond order increases, the bond length decreases.
What is the impact of resonance on bond length?
Resonance can lead to the equalization of bond lengths in a molecule, resulting in shorter and more uniform bond lengths.