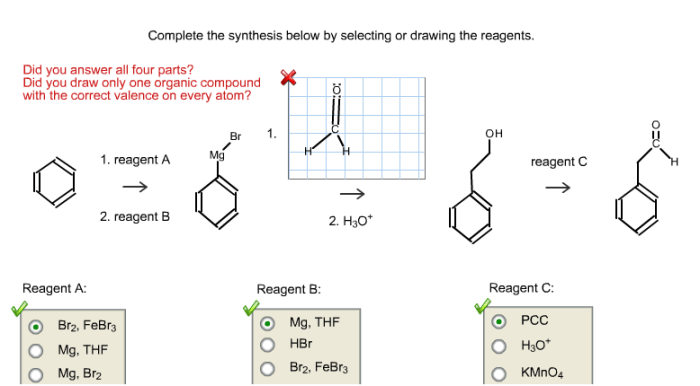
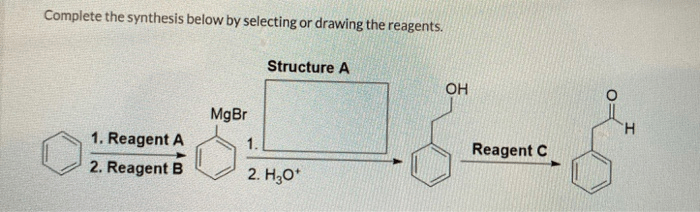
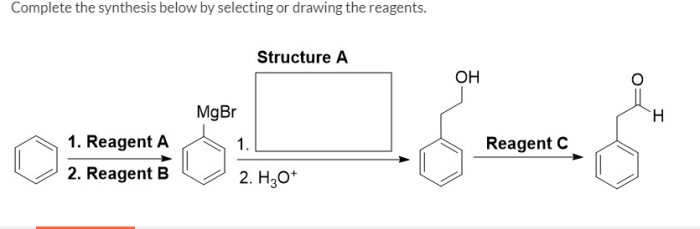
Complete the synthesis below by selecting or drawing the reagents. In the realm of chemical synthesis, the judicious selection and representation of reagents play a pivotal role in orchestrating successful reactions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of reagent selection, empowering chemists with the knowledge and techniques to navigate the vast landscape of chemical possibilities.
The discourse encompasses the factors governing reagent choice, the diverse methods employed for reagent depiction, and the systematic procedures guiding the decision-making process. Through a tapestry of illustrative examples and practical guidance, this discourse illuminates the art and science of reagent selection, equipping chemists with the tools to conquer the challenges of chemical synthesis.
Selecting or Drawing Reagents for Chemical Synthesis: Complete The Synthesis Below By Selecting Or Drawing The Reagents.
Selecting or drawing reagents is a crucial step in chemical synthesis. The choice of reagents depends on various factors, including their reactivity, selectivity, and availability. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the process of selecting or drawing reagents, discussing the factors to consider and the techniques used.
Examples of Reagent Selection
The selection of reagents for specific chemical reactions is based on their properties and the desired outcome. Here are some examples:
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions:Strong nucleophiles like sodium hydride (NaH) or potassium tert-butoxide (t-BuOK) are used for reactions with alkyl halides.
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions:Electrophiles like bromine (Br2) or nitric acid (HNO3) are used for reactions with aromatic compounds.
- Condensation reactions:Carboxylic acids and alcohols can be condensed using reagents like dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) or 1,1′-carbonyldiimidazole (CDI).
Methods for Drawing Reagents
Reagents can be drawn using various methods:
- Structural formulas:Lewis structures or condensed structural formulas represent the molecular structure of reagents using symbols and lines.
- Molecular models:Ball-and-stick or space-filling models provide a 3D representation of the reagent’s structure.
- Computer-aided drawing software:Specialized software like ChemDraw or MarvinSketch allows for the precise drawing and manipulation of chemical structures.
Procedures for Selecting or Drawing Reagents, Complete the synthesis below by selecting or drawing the reagents.
The selection or drawing of reagents involves a systematic approach:
- Identify the desired reaction:Determine the target product and the type of reaction required.
- Research reagent options:Explore databases or literature to find suitable reagents.
- Consider reactivity and selectivity:Choose reagents that react efficiently and selectively to minimize side reactions.
- Check availability and cost:Ensure the reagents are readily available and cost-effective.
- Draw the reagent structures:Use the appropriate method to represent the molecular structures of the selected reagents.
Essential FAQs
What factors should be considered when selecting reagents?
Reactivity, selectivity, availability, cost, safety, and environmental impact are key factors to consider.
What methods can be used to draw reagents?
Structural formulas, molecular models, and computer-aided drawing software are commonly used methods.
Why is it important to document the reagent selection process?
Documentation ensures reproducibility, facilitates collaboration, and provides a record of the decision-making process.